Types of Mortgage

Option 1: Fixed vs. Adjustable Rate
As a borrower, one of your first choices is whether you want a fixed-rate or an adjustable-rate mortgage loan. All loans fit into one of these two categories, or a combination "hybrid" category. Here's the primary difference between the two types:
- Fixed-rate mortgage loans have the same interest rate for the entire repayment term. Because of this, the size of your monthly payment will stay the same, month after month, and year after year. It will never change. This is true even for long-term financing options, such as the 30-year fixed-rate loan. It has the same interest rate, and the same monthly payment, for the entire term.
- Adjustable-rate mortgage loans (ARMs) have an interest rate that will change or "adjust" from time to time. Typically, the rate on an ARM will change every year after an initial period of remaining fixed. It is therefore referred to as a "hybrid" product. A hybrid ARM loan is one that starts off with a fixed or unchanging interest rate, before switching over to an adjustable rate. For instance, the 5/1 ARM loan carries a fixed rate of interest for the first five years, after which it begins to adjust every one year, or annually. That's what the 5 and the 1 signify in the name.
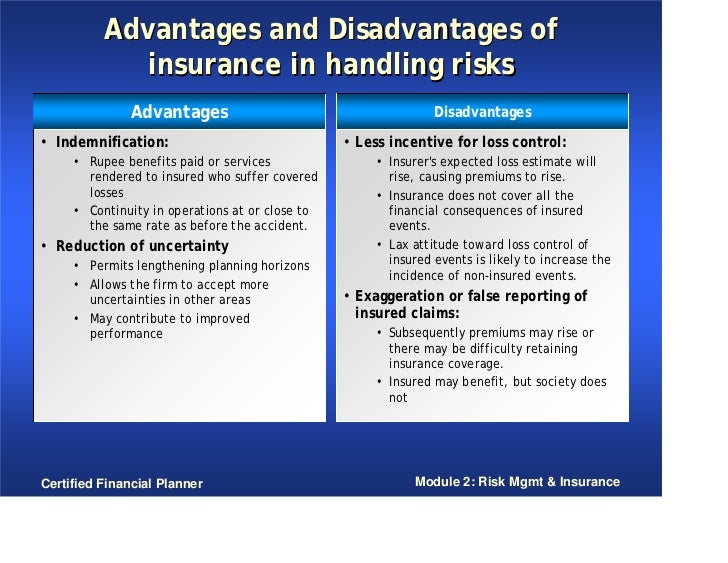
Pros and cons: adjustable V/S fixed-rate mortgages
As you might imagine, both of these types of mortgages have certain pros and cons associated with them. Use the link above for a side-by-side comparison of these pros and cons. Here they are in a nutshell: The ARM loan starts off with a lower rate than the fixed type of loan, but it has the uncertainty of adjustments later on. With an adjustable mortgage product, the rate and monthly payments can rise over time. The primary benefit of a fixed loan is that the rate and monthly payments never change. But you will pay for that stability through higher interest charges, when compared to the initial rate of an ARM.
Option 2: Government-Insured vs. Conventional Loans
So you'll have to choose between a fixed and adjustable-rate type of mortgage, as explained in the previous section. But there are other choices as well. You'll also have to decide whether you want to use a government-insured home loan (such as FHA or VA), or a conventional "regular" type of loan. The differences between these two mortgage types are covered below.
A conventional home loan is one that is not insured or guaranteed by the federal government in any way. This distinguishes it from the three government-backed mortgage types explained below (FHA, VA and USDA).
Government-insured home loans include the following:
FHA Loans
The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) mortgage insurance program is managed by the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), which is a department of the federal government. FHA loans are available to all types of borrowers, not just first-time buyers. The government insures the lender against losses that might result from borrower default. Advantage: This program allows you to make a down payment as low as 3.5% of the purchase price. Disadvantage: You'll have to pay for mortgage insurance, which will increase the size of your monthly payments.
The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) mortgage insurance program is managed by the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), which is a department of the federal government. FHA loans are available to all types of borrowers, not just first-time buyers. The government insures the lender against losses that might result from borrower default. Advantage: This program allows you to make a down payment as low as 3.5% of the purchase price. Disadvantage: You'll have to pay for mortgage insurance, which will increase the size of your monthly payments.
See also: Pros and cons of FHA vs. conventional
VA Loans
The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) offers a loan program to military service members and their families. Similar to the FHA program, these types of mortgages are guaranteed by the federal government. This means the VA will reimburse the lender for any losses that may result from borrower default. The primary advantage of this program (and it's a big one) is that borrowers can receive 100% financing for the purchase of a home. That means no down payment whatsoever.
Learn more: VA loan eligibility requirements
The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) offers a loan program to military service members and their families. Similar to the FHA program, these types of mortgages are guaranteed by the federal government. This means the VA will reimburse the lender for any losses that may result from borrower default. The primary advantage of this program (and it's a big one) is that borrowers can receive 100% financing for the purchase of a home. That means no down payment whatsoever.
Learn more: VA loan eligibility requirements
USDA / RHS Loans
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) offers a loan program for rural borrowers who meet certain income requirements. The program is managed by the Rural Housing Service (RHS), which is part of the Department of Agriculture. This type of mortgage loan is offered to "rural residents who have a steady, low or modest income, and yet are unable to obtain adequate housing through conventional financing." Income must be no higher than 115% of the adjusted area median income [AMI]. The AMI varies by county. See the link below for details.
Learn more: USDA borrower eligibility website
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) offers a loan program for rural borrowers who meet certain income requirements. The program is managed by the Rural Housing Service (RHS), which is part of the Department of Agriculture. This type of mortgage loan is offered to "rural residents who have a steady, low or modest income, and yet are unable to obtain adequate housing through conventional financing." Income must be no higher than 115% of the adjusted area median income [AMI]. The AMI varies by county. See the link below for details.
Learn more: USDA borrower eligibility website
Combining: It's important to note that borrowers can combine the types of mortgage types explained above. For example, you might choose an FHA loan with a fixed interest rate, or a conventional home loan with an adjustable rate (ARM).
Option 3: Jumbo vs. Conforming Loan
There is another distinction that needs to be made, and it's based on the size of the loan. Depending on the amount you are trying to borrow, you might fall into either the jumbo or conforming category. Here's the difference between these two mortgage types.
- A conforming loan is one that meets the underwriting guidelines of Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac, particularly where size is concerned. Fannie and Freddie are the two government-controlled corporations that purchase and sell mortgage-backed securities (MBS). Simply put, they buy loans from the lenders who generate them, and then sell them to investors via Wall Street. A conforming loan falls within their maximum size limits, and otherwise "conforms" to pre-established criteria.
- A jumbo loan, on the other hand, exceeds the conforming loan limits established by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. This type of mortgage represents a higher risk for the lender, mainly due to its size. As a result, jumbo borrowers typically must have excellent credit and larger down payments, when compared to conforming loans. Interest rates are generally higher with the jumbo products, as well.