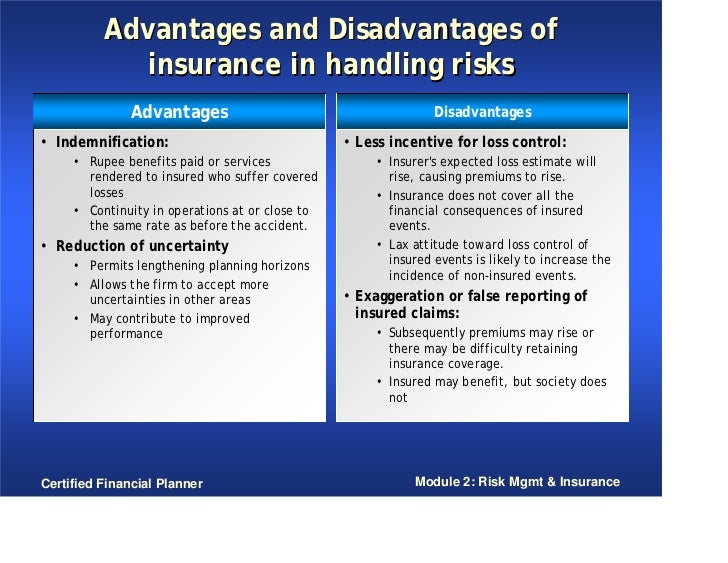
Advantages & disadvantages of Life Insurance Advantages of Life Insurance
Advantages of Life Insurance
1. Economic protection against the loss of life. The emotional loss caused to the family of the insured cannot be measured in terms of money. However, the financial responsibility of the insured towards his family members are to an extent shared by the Life insurers. On the death of the insured, the family will have some money to continue having a comfortable life. The life insurance policy provides an option to choose the nominee.
2. A form of investment or saving. Many people buy life insurance as part of their investments. Most insurance policies guarantees a fixed sum of money payable either on the death of the insured or at the expire of the pre-determined tenure. Hence, many people keep aside a part of their savings for the payment of Life insurance premium in the form of investment.
3. Life insurance is simple to understand in terms of premium and the maturity of the compensation. The investment amount, policy term, and the maturity amount are clearly mentioned on the policy document.
4. Some Life insurance policies are flexible. The give the insured an option to change the policy amount with the change in his needs. When the insurance needs of the insured changes, they can talk to the insurer so that they can adjust their insurance plan. However, it should be kept in mind that not all insurance policies are flexible enough to satisfy the ever-changing need of the policy holder. Hence, the policy buyer should read all the term and conditions of the policy at the time of first purchase.
5. Loan against Life Insurance Policies (LAIP) is a newest form of financial revolution. Many financial institutions offer loan against the surrender value of the insurance policy. This a safe and quick way to generate cash.
6. The insured pays the premium depending on the sum insured. Depending on the age of the insured, they can select the amount they want to pay per month that won’t be a burden to them.
7. Enable the insured to be able to select their beneficiary. When buying a policy, one has to choose who the beneficiary of the insurance policy will be. In this way, they make sure that the material needs of their loves ones would always be met.
8. Reduces the financial implication of death. Life insurance reduces the financial burden that comes with the death of the breadwinner.
9. There is a range of policies to choose from. Life insurance has a range of policies to choose from. In some policies, one is compensated when a certain period of time elapses.
10. Tax saving weapon. In most countries, the final amount that you get from the insurer is not taxable. In India, the amount of Life insurance policy premiums are allowed as deduction under section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961. The maturity proceeds are also exempted from Income Tax. Hence, investment in a life insurance policy is an amazing tax saving weapon.
Disadvantages of Life Insurance
1. Insurance policies are expensive. Life insurance means that you have to contribute your premium until you die or a fixed tenure that is very long. This will be expensive for the insured. The part of the life insurance premium paid towards risk coverage is an expense. However, the quantum of financial risk mitigated by these policies are much more than these expenses. Hence, people treat life insurance premiums as mandatory expense.
2. Some insurance companies may refuse to pay the sum insured. Some insurers will use dirty tricks to evade the pay the sum insured even after maturity of the policy. For this reason, it is important that you read all the clauses of the life policy at the time of entering into the contract. Further, you can consult your financial advisor before buying a policy.
3. People buying the insurance they don’t need. Some people may buy the insurance policy when they don’t need one. Paying for a policy that do not meet the need of the paying person is a waste of money.
4. Some people give falsified information. Some people give false information to the insurance company e.g., age leading to the insurer making losses.
5. The beneficiary may decide to waste the amount they receive. The beneficiary may not use the funds as it was intended leading to wastage of the sum insured.
6. Many life insurance policies keep on changing. In such policies, the premium amount is low during the initial years. However, the premium amount do not remain constant. They keep changing with time. You may be required to pay more premium as you grow older than when you were young.
7. Having it doesn’t necessarily mean better quality of life. Life insurance may mean poor quality of life to be able to pay the premium. The deduction may be too many.
8. There are so many complex insurance policies. The insurance policies are complex that one may not be able to understand. There are ‘good’ and there are ‘not so good’ insurance companies. Similarly, there are some ‘not so simple’ insurance policies that is beyond the understanding capability of a common man. Hence, it can be a very daunting task to choose the right life policy.
9. The investment is not highly paying. Life insurance is primarily an instrument to cover risk. The investment function is of secondary nature. Unlike other types of investment that have high returns, life insurance does not give high returns. Hence, people seeking high return on their investment may not find it attractive for investment.